
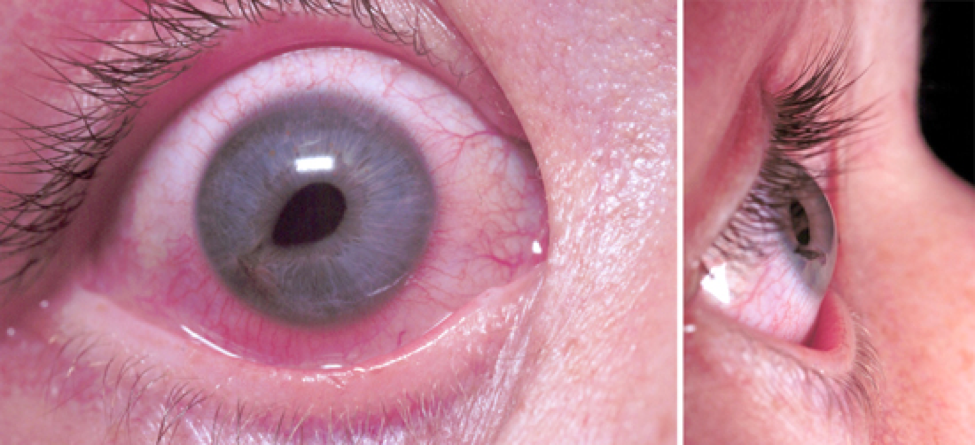
LifeFlight Retrieval Medicine (LRM) is an aeromedical service that operates across Queensland, Australia. There are constraints on positioning patients in the upright position to facilitate IOP measurement, such as spinal immobilisation and aircraft configuration. Use of a tonometer, a key diagnostic hospital tool, is not practical in the aeromedical setting where there are limitations on equipment including weight, size and durability. Prehospital kits including in our organisation do not contain visual acuity charts and tonometry devices. There may be limitation on personnel availability to retract tense eyelids for inspection of the orbit. Patient factors include the presence of concomitant head injury resulting in altered level of consciousness and rendering meaningful assessment of visual acuity and orbital movements impossible. Environmental factors include variable light, space limitations, vibrations in the helicopter and noise. One key principle of prehospital trauma management is to limit scene times and deliver patients to definitive care as soon as possible, thereby limiting assessment and interventions to those that add immediate value to the patient's care. In the prehospital setting, the challenges faced by retrieval clinicians include time pressures, competing clinical interests, inability to assess visual acuity due to both patient and scene factors, absence of tonometer to measure IOP, lack of focused training to perform the procedure and limitations on the equipment available to perform LCC. Lateral canthotomy and cantholysis (LCC) is the standard treatment to decompress the orbit and performing LCC within 2 h is associated with good visual outcomes. The key clinical features of OCS are reduced visual acuity, proptosis, restricted extraocular movements, relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD) and raised intraocular pressure (IOP). To prevent irreversible eye damage, OCS requires urgent diagnosis and treatment, both of which are challenging in the prehospital environment. Orbital compartment syndrome (OCS) is an ophthalmic emergency, characterised by raised intra-orbital pressure and subsequent ocular ischemia.

Aeromedical clinicians should be familiar with, trained for, and have access to equipment to perform LCC.Prehospital LCC may be required in the Australian aeromedical context given long transfer times.If a patient cannot be delivered to a hospital with staff trained in LCC in a timeframe under 90–120 min post injury, prehospital LCC is indicated and should not be delayed. LCC is a time sensitive, vision saving procedure.They should be provided with suitable training and supported by a standard operating procedure. It is important that prehospital physicians have access to appropriate equipment to perform LCC. Clinical diagnosis and management of OCS are highly challenging in the prehospital setting. The Australian aeromedical context often involves lengthy transfers of trauma patients. Clinical findings, aeromedical considerations, and radiological findings at the receiving facility, along with visual outcomes at time of discharge are discussed. LCC was performed at the primary scene in two cases, while one patient underwent LCC at a rural hospital near the scene of injury. Three cases out of 7413 trauma missions were identified over the 5-year period. We performed a retrospective audit of LCC in our service from January 2016 to December 2020 by retrieving demographic and clinical details from LifeFlight Retrieval Medicine electronic database using ‘OCS’ and ‘LCC’ as keywords. This study aims to provide learning points on performing lateral canthotomy and cantholysis (LCC) in the prehospital setting.

In the prehospital setting, the diagnosis and management of OCS is challenging due to complex environmental considerations, competing clinical priorities, and limited equipment. Orbital compartment syndrome (OCS) is a time critical condition, with ischaemic complications occurring after 90–120 min.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
